Vulnerabilities and patch management
Codebase
RailLab and its services’ codebase are maintained by a team of salaried developers (us!) working exclusively and full time for Rail Concept
We do not employ external contractors and our codebase is private and only accessible to our team
Maybe because we have a narrow and specialized target audience, we have yet to receive a vulnerability notice from an external or internal user or consultant
Anyone who find a vulnerability should contact us at r.blin@railconcept.fr
RailLab
We maintain RailLab up to date with the latest LTS (Long Term Support) .NET version available
Since we develop RailLab very actively, the latest released version should always be up to date with current libraries and framework
We do scan our RailLab binaries with VirusTotal before sending any version of RailLab to our client
If a vendor raise a detection, we do investigate if it is founded or not and decide accordingly if we should proceed with the release
Usualy warnings are due to the self contained single file publish mode from the .NET from the setups but we haven’t had much issues since we implemented the signature on every bundled binary
Examples of reports:
Web services (RC License API)
We maintain our services up to date with the latest LTS (Long Term Support) .NET version available for each Azure service we use (Azure Web Apps, Azure Functions and Azure Static Web Apps so far)
While the development of these services may be a bit slower, we do check for framework and library updates at least once a month
There is only one official production version of each service available through their official domain (e.g.: api.license.railconcept.fr for RC License API)
We never run different codebase of the same service at once in production, only for internal testing with staging versions (those versions are not available to our client or the public)
Framework, tools and libraries vulnerabilities
RailLab is a desktop software developed in C#.NET
Its framework is .NET 10, WPF and uses some FOSS libraries
All libraries not included in the .NET SDK is installed using NuGet and are listed in the FOSS libraries list section
Vulnerability watch
We keep track of deprecated and vulnerables libraries and frameworks through the following tools:
- Visual Studio NuGet Package Manager:
We use this tool every ~3 work days to check for library update and do update right away obsolete and vulnerable NuGet packages
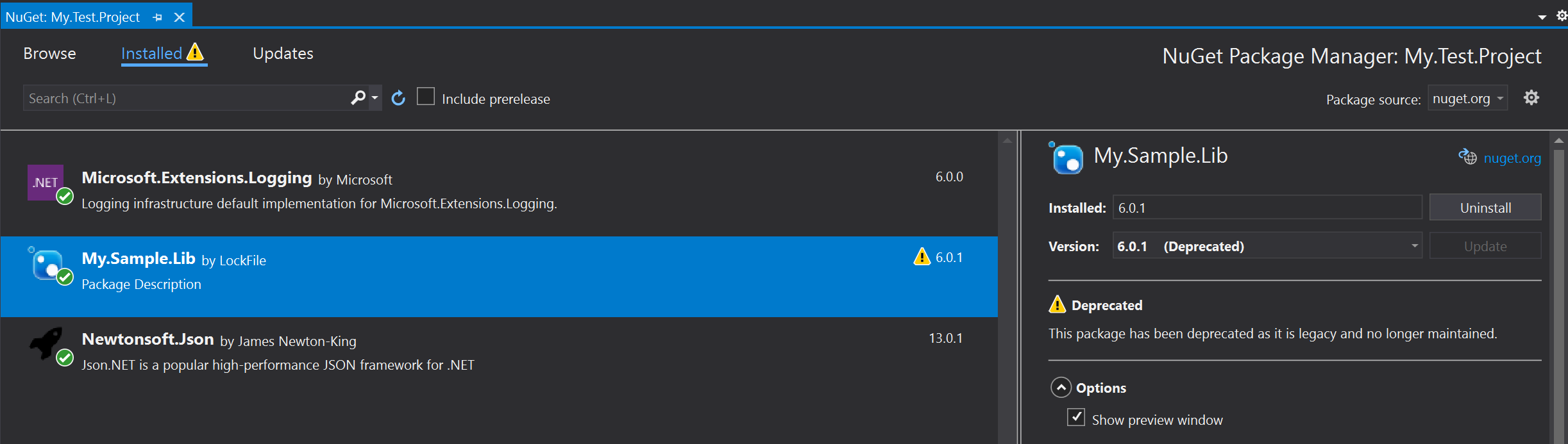
Illustration taken from https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/nuget/nuget-org/deprecate-packages dotnet list package --vulnerableanddotnet list package --vulnerable
We integrated these commands in our release pipeline to raise a warning
We do check every release pipeline result for any warning and cancel the release and address the warning before re-releasing again- The .NET changelog we consult at least once a month
- Vulnerability and deprecation notice sent by emails from Microsoft for our IDE (Visual Studio), Azure services and the .NET framework
FOSS libraries list
For transparency here’s a list of all third party libraries we use in RailLab:
| Reference | Version | License Type | License |
|---|---|---|---|
| Castle.Core | 5.2.1 | Apache-2.0 | https://licenses.nuget.org/Apache-2.0 |
| Castle.Core-Serilog | 5.2.1 | Apache-2.0 | https://licenses.nuget.org/Apache-2.0 |
| Castle.LoggingFacility | 6.0.0 | Apache-2.0 | http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0.html |
| Castle.Windsor | 6.0.0 | Apache-2.0 | http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0.html |
| DiffLib | 2025.0.0 | LICENSE.md | https://www.nuget.org/packages/DiffLib/2025.0.0/License |
| DocumentFormat.OpenXml | 3.4.1 | MIT | https://licenses.nuget.org/MIT |
| DynamicData | 9.4.1 | MIT | https://licenses.nuget.org/MIT |
| Dynamitey | 3.0.3 | Apache-2.0 | http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 |
| F23.StringSimilarity | 7.0.1 | MIT | https://licenses.nuget.org/MIT |
| gong-wpf-dragdrop | 4.0.0 | LICENSE | https://www.nuget.org/packages/gong-wpf-dragdrop/4.0.0/License |
| HtmlTableHelper | 1.2.4 | Apache-2.0 | https://licenses.nuget.org/Apache-2.0 |
| ImpromptuInterface | 8.0.6 | Apache-2.0 | https://licenses.nuget.org/Apache-2.0 |
| Jamarino.IntervalTree | 1.2.2 | LICENSE.md | https://www.nuget.org/packages/Jamarino.IntervalTree/1.2.2/License |
| JsonKnownTypes | 0.7.0 | LICENSE | https://www.nuget.org/packages/JsonKnownTypes/0.7.0/License |
| LibGit2Sharp | 0.31.0 | App_Readme/LICENSE.md | https://www.nuget.org/packages/LibGit2Sharp/0.31.0/License |
| MahApps.Metro | 2.4.11 | MIT | https://licenses.nuget.org/MIT |
| MaterialDesignThemes | 5.3.0 | MIT | https://licenses.nuget.org/MIT |
| MaterialDesignThemes.MahApps | 5.3.0 | MIT | https://licenses.nuget.org/MIT |
| Microsoft.Identity.Client | 4.81.0 | MIT | https://licenses.nuget.org/MIT |
| Microsoft.Identity.Client.Broker | 4.81.0 | MIT | https://licenses.nuget.org/MIT |
| Microsoft.Identity.Client.Desktop | 4.81.0 | MIT | https://licenses.nuget.org/MIT |
| Microsoft.Identity.Client.Extensions.Msal | 4.81.0 | MIT | https://licenses.nuget.org/MIT |
| Microsoft.IdentityModel.LoggingExtensions | 8.15.0 | MIT | https://licenses.nuget.org/MIT |
| Microsoft.Xaml.Behaviors.Wpf | 1.1.135 | MIT | https://licenses.nuget.org/MIT |
| morelinq | 4.4.0 | COPYING.txt | https://www.nuget.org/packages/morelinq/4.4.0/License |
| Newtonsoft.Json | 13.0.4 | MIT | https://licenses.nuget.org/MIT |
| Ookii.Dialogs.Wpf | 5.0.1 | BSD-3-Clause | https://licenses.nuget.org/BSD-3-Clause |
| PowerArgs | 4.0.3 | MIT | https://licenses.nuget.org/MIT |
| RBush | 4.0.0 | MIT | https://licenses.nuget.org/MIT |
| ScottPlot.WPF | 5.1.57 | MIT | https://licenses.nuget.org/MIT |
| Serilog.Enrichers.Environment | 3.0.1 | Apache-2.0 | https://licenses.nuget.org/Apache-2.0 |
| Serilog.Enrichers.Process | 3.0.0 | Apache-2.0 | https://licenses.nuget.org/Apache-2.0 |
| Serilog.Enrichers.Thread | 4.0.0 | Apache-2.0 | https://licenses.nuget.org/Apache-2.0 |
| Serilog.Exceptions | 8.4.0+build.694 | MIT | https://licenses.nuget.org/MIT |
| Serilog.Extensions.Logging | 10.0.0 | Apache-2.0 | https://licenses.nuget.org/Apache-2.0 |
| Serilog.Formatting.Compact | 3.0.0 | Apache-2.0 | https://licenses.nuget.org/Apache-2.0 |
| Serilog.Formatting.Compact.Reader | 4.0.0 | Apache-2.0 | https://licenses.nuget.org/Apache-2.0 |
| Serilog.Sinks.Async | 2.1.0 | Apache-2.0 | https://licenses.nuget.org/Apache-2.0 |
| Serilog.Sinks.Console | 6.1.1 | Apache-2.0 | https://licenses.nuget.org/Apache-2.0 |
| Serilog.Sinks.Debug | 3.0.0 | Apache-2.0 | https://licenses.nuget.org/Apache-2.0 |
| Serilog.Sinks.File | 7.0.0 | Apache-2.0 | https://licenses.nuget.org/Apache-2.0 |
| SerilogTraceListener | 3.2.0 | Apache-2.0 | https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 |
| SharpCompress | 0.44.5 | MIT | https://licenses.nuget.org/MIT |
| SkiaSharp.Views.WPF | 3.119.1 | MIT | https://licenses.nuget.org/MIT |
| Slugify.Core | 5.1.1 | MIT | https://licenses.nuget.org/MIT |
| System.ComponentModel.Annotations | 5.0.0 | MIT | https://licenses.nuget.org/MIT |
| System.Data.DataSetExtensions | 4.5.0 | MIT | https://github.com/dotnet/corefx/blob/master/LICENSE.TXT |
| System.IdentityModel.Tokens.Jwt | 8.15.0 | MIT | https://licenses.nuget.org/MIT |
| System.Linq.Async | 7.0.0 | MIT | https://licenses.nuget.org/MIT |
| System.Management | 10.0.2 | MIT | https://licenses.nuget.org/MIT |
| System.Reactive | 6.1.0 | MIT | https://licenses.nuget.org/MIT |
| System.ServiceModel.Duplex | 6.0.0 | MIT | https://licenses.nuget.org/MIT |
| System.ServiceModel.Federation | 10.0.652802 | MIT | https://licenses.nuget.org/MIT |
| System.ServiceModel.Http | 10.0.652802 | MIT | https://licenses.nuget.org/MIT |
| System.ServiceModel.NetTcp | 10.0.652802 | MIT | https://licenses.nuget.org/MIT |
| System.ServiceModel.Security | 6.0.0 | MIT | https://licenses.nuget.org/MIT |
| WinForms.DataVisualization | 1.10.0 | MIT | https://licenses.nuget.org/MIT |
This list is up to date with the 1.2.30 version, it is a static list that we renew it everytime we update this documentation
Vulnerability and obsoletion notices
Rolling releases
We do always recommend running and upgrading to the latest RailLab version that fits your use case
We understand that some of our users are locked with an older RailLab version for domain (train exploitation) related reasons and we do provide support for them
If you ever rely on a Release build that suffers from known vulnerabilities we will either:
- Assist you upgrading to latest
Releaseif no breaking change happened since - Revalidate a new
Releaseif breaking changes happened - If locked on a version for domain related reasons we can release a new
Releaseversion with patched vulnerabilities on the same major feature version
For others channels we will ask you to upgrade to a newly released version
Notifying users
When we detect a vulnerable or obsolete version we mark it as such with a report in the markdown format
This file is complementary to the changelog and when existing can be found:
- On download.raillab.fr

- In the RLauncher
We also notify all our client that may be affected by:
- Formally using your primary contact email, if provided a dedicated email address we will use this one
- Informally by Teams to assist you upgrade and find solutions
Service level agreements
Vulnerabilities are covered under the same SLA as malfunctions described in Resilience considerations - Service levels agreements
This SLA covers:
- The latest available version of RailLab
- Our clients’ RailLab in-production versions
- The current in-production RC License API
Risk assessment
While RailLab as a desktop software remains fairly isolated from most common attack vectors there is always some hazards we can identify, evaluate their exposure and impacts and how we mitigate them and what improvement should be done within what timeframe
We only describe hazards from a cyber-security standpoint and not from a general safety standpoint in order to stay within the context of this document
Note: Hazards described are completely hypothetical in order to assess the risk, we do not have history of such attacks vectors using RailLab nor actual practical evidence of reproducibility
Supply chain attack
Hazard
- This attack would happen by hijacking the CI/CD process or the binaries storage and allowing the attacker to distribute malicious versions of the files
- The hijack could happen by stealing a developer session or password or a platform related vulnerability
- The same attack could happen to a library RailLab uses with the same exposure and impact to users
Exposure
- Users who happens to install a new version before the attack is addressed
Impact evaluation
- Equivalent to a trojan: compromised user system, takeover with potential privilege escalation
Mitigation mechanisms
- Every developer account requires a 2FA and a strong password
- Triggering a CI/CD pipeline can only be done with the approval of developer with the specific privileges
- Binaries are signed so manipulating the existing binaries or emitting unsigned binaries should raise a SmartScreen warning
- We have internal communication channels for announcing a release along its changes which would make the release very suspicious
- RailLab and RLauncher always run with normal (non-privileged) user rights
Conclusion
This hazard would have the most impact of all because running malicious code is almost always the worst case scenario
Considering its mitigations mechanism we judge this risk happening as unlikely with low exposure but it has the highest impact
Rating: Medium
Malicious manipulation of data files
Hazard
- An attacker could manipulate a database (.rlab) or any similar file to exploit a RailLab vulnerability leading to potential arbitrary code execution
- The attacker would impersonate a person of trust to the target and send the file by private communication like Teams or by email
Exposure
- Users who exchanges databases often by email or Teams and whose their contacts recently got impersonated
Impact evaluation
- Equivalent to remote code execution: compromised user system, takeover with potential privilege escalation
Mitigation mechanisms
- Databases have prorietary control sum checks
- RailLab rely on standard .NET de/serializers that sanitize their input/output
- RailLab is developed in C#.NET which is memory safe, benefits for memory allocation randomization which makes arbitrary code execution more difficult
Conclusion
The high technicality required to exploit the vulnerability mixed with the low impact, low exposure and strong mitigations makes us judge this hazard’s risk as low
Rating: Low
API takeover
Hazard
- An attacker could impersonate a service (for instance RC License API) either by complete service takeover (for instance by leveraging a supply chain attack) or a MitM attack, and emit malicious HTTP responses or deny the service
Exposure
- Users who launch RailLab
Impact evaluation
- Deny acquisition and refresh of licenses for users, those users will get an error and if no refresh happened for the last week will not be able to launch RailLab
- Potentially be able to execute code (equivalent to supply chain attack’s impact) if: RailLab and its de/serializers and its HTTP client library are also vulnerable
Mitigation mechanisms
- Azure Public Cloud security mechanism for protecting Web Apps
- It is very obvious since RailLab will notify when the license could not be revalidated
- All our services CI/CD releases are protected in the same way as described in the supply chain attack’s mitigation mechanisms section
Conclusion
We separated this hazard in two versions: with or without code injection
No code injection is more likely because it requires less potential combined vulnerabilities, has more exposure but the least impact
With code injection has the highest impact combined with highest exposure but requires a lot of potential combined vulnerabilities
Rating:
- Low without code injection
- Medium if combined with code injection
Risk evaluation table
This is a table summarizing our subjective evaluation of risks
Evaluation of probability or impact is relative to the project and not an absolute metric confonding every element of the information system RailLab is installed
| Impact → Probability ↓ | Very low | Low | Medium | High | Maximal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Very low | Malicious manipulation of data files | API takeover (with code injection) | |||
| Low | Supply chain attack | ||||
| Medium | API takeover (no code injection) | ||||
| High | |||||
| Maximal |